A manifold gauge is an essential tool used in the heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration (HVAC-R) industry for diagnosing and maintaining refrigeration and air conditioning systems. It allows technicians to measure the pressure inside the system and is often used in conjunction with other tools like vacuum pumps and refrigerant scales. This device plays a crucial role in ensuring the proper functioning of air conditioning units, refrigerators, and other cooling systems by helping professionals analyze pressure levels and refrigerant flow.
1. Purpose and Functionality
The primary function of a manifold gauge is to measure the pressure within refrigeration or air conditioning systems. It enables technicians to assess the status of the refrigerant in the system by providing readings for both low and high-pressure sides. These readings are crucial for troubleshooting, maintenance, and ensuring good system performance.
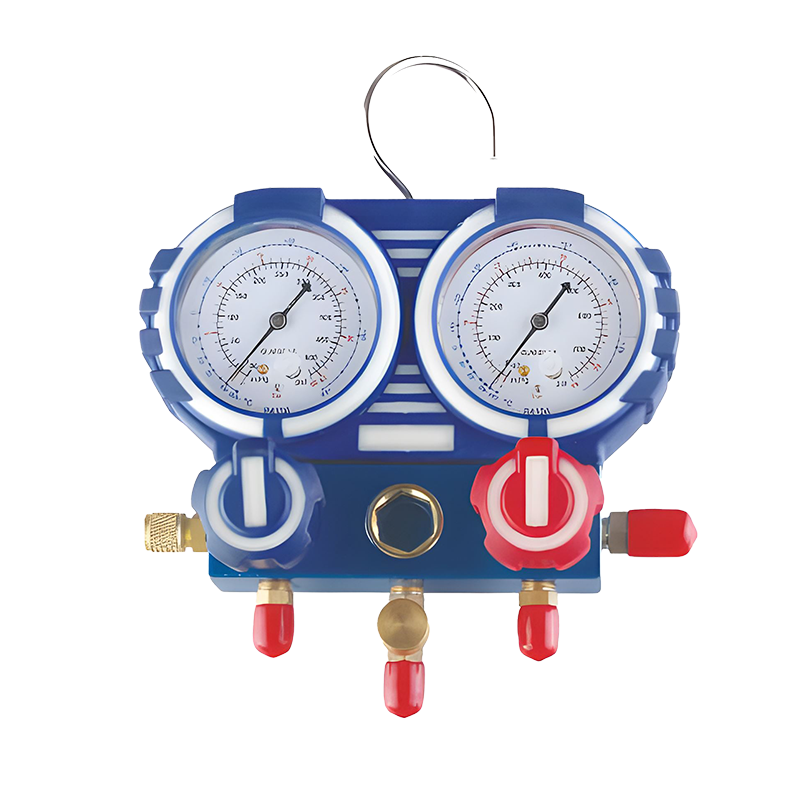
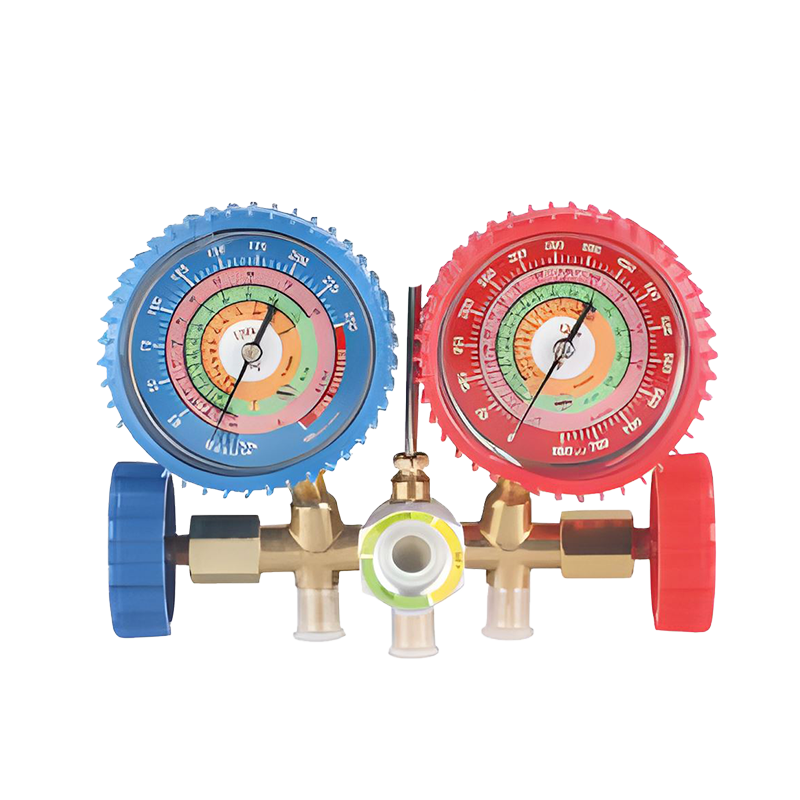
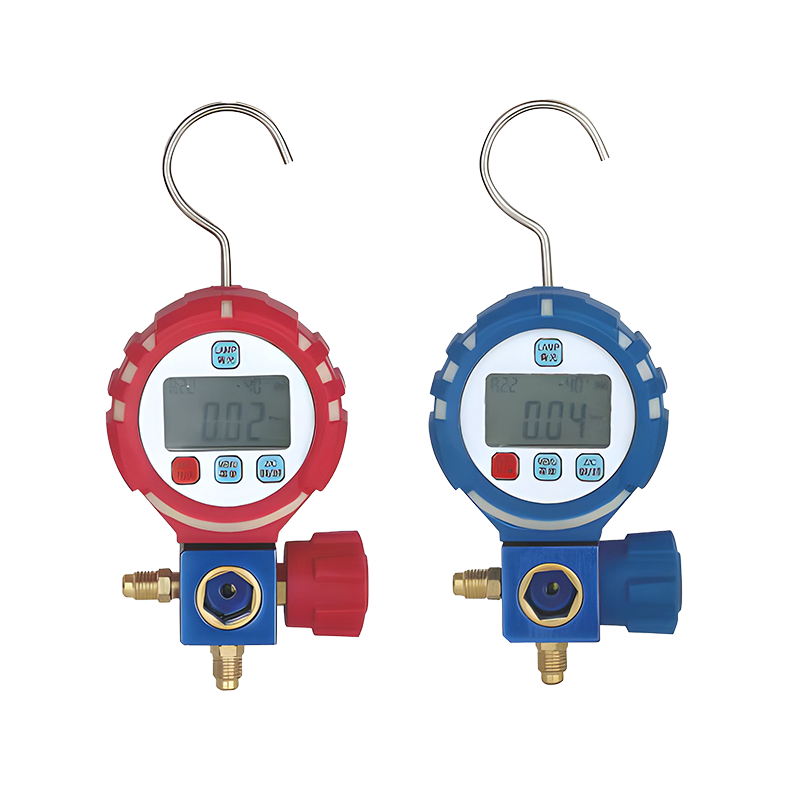
Pressure Measurement: Manifold gauges typically come with two pressure gauges, one for the low side and one for the high side of the refrigeration system. These gauges measure the pressure of the refrigerant in pounds per square inch (PSI) and provide vital information about the system’s operating conditions.
Refrigerant Flow Monitoring: The manifold gauge enables technicians to observe the flow of refrigerants within the system, helping them detect any leaks, blockages, or inefficiencies that could impact system performance.
2. Key Features
Manifold gauges come with several features designed to improve accuracy, durability, and ease of use:
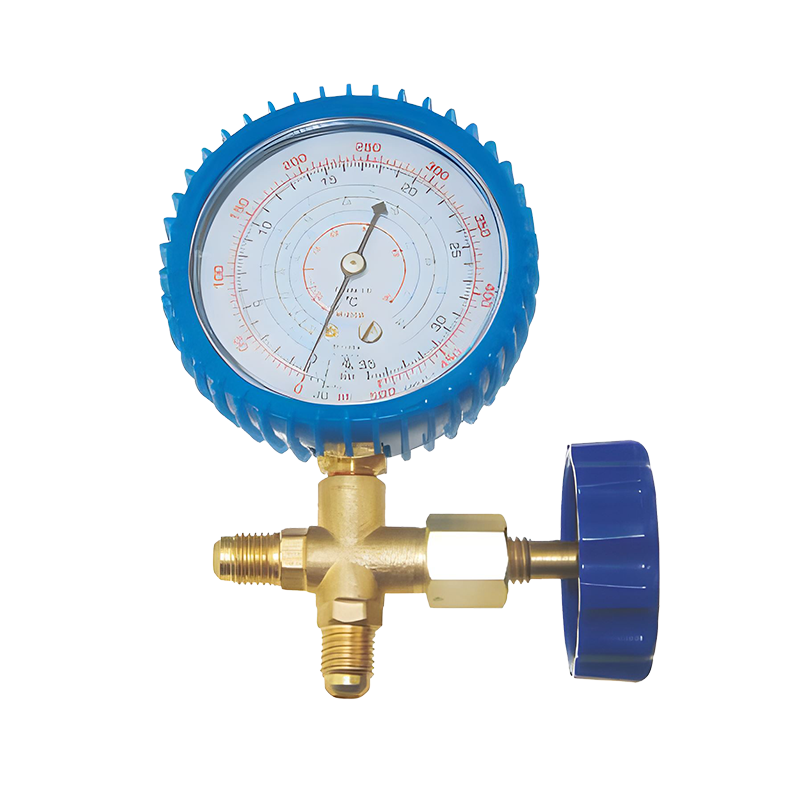
Dual Pressure Gauges: Manifold gauges feature two separate pressure gauges, which allow the technician to measure both the high and low sides of the system. The low-pressure gauge is typically used for the evaporator side, while the high-pressure gauge is used for the compressor side.
Color-Coded Hoses: manifold gauges are equipped with color-coded hoses (typically blue for low-pressure side, red for high-pressure side, and yellow for refrigerant recovery or charging). This color-coding ensures that technicians can easily identify the correct hose for each application, preventing any cross-contamination or misuse.
Heavy-Duty Construction: A quality manifold gauge is made of durable materials, often with brass or aluminum construction, to withstand the pressures and environments associated with HVAC and refrigeration applications. This ensures longevity and reliability.
Pressure Relief Valve: A built-in relief valve helps prevent system damage by releasing excess pressure in case of a malfunction or overcharging.
High and Low-Pressure Readouts: Accurate digital or analog readouts on the gauge face allow the technician to quickly interpret the system’s pressure status and make adjustments as needed.
3. Applications
Manifold gauges are widely used in various applications within the HVAC and refrigeration industries:
System Diagnostics and Troubleshooting: Technicians use manifold gauges to diagnose issues within refrigeration and air conditioning systems. If the pressure readings are too high or too low, it could indicate issues such as overcharging, undercharging, or refrigerant leaks.
Refrigerant Charging: When a system requires additional refrigerant, the manifold gauge is used to ensure the proper amount is added. The technician will use the gauge to measure the system’s pressure and compare it to the manufacturer’s specifications for the refrigerant charge.
Vacuum Testing and Evacuation: Manifold gauges are also used during the evacuation process of an HVAC or refrigeration system. This involves removing any moisture or air from the system before adding refrigerant. The gauge helps confirm that the system is adequately evacuated.
Refrigerant Recovery: During servicing or repair, when refrigerants need to be recovered from the system, manifold gauges ensure the proper handling of refrigerants and confirm that no harmful gas is released into the atmosphere.